One Minute Course in PMP
What is PMP?
PMP Stands for Project Management Professional, a certification provided by the Project Management Institute PMI ( www.PMI.org ), for those who want to prove a professional level in project management.
As I’m writing this document in April 2023, there are more than 1.2 million professionals around the world certified PMP.
Most of excellent project management jobs are now listing PMP as one of their main criteria for selecting professionals for that job.
One of the most important aspects of PMP is that it is not limited to a certain field of specialization. It is applicable in fields like construction, IT and many other fields.
PMP Exam Requirements
Following are the criteria to be eligible for the PMP Exam:
1. 35 hours of project management training.
2. Work Experience as in the following table:
| Degree |
Years PM Experience in a leadership position in project management within 8 years of PMP Application Data: |
|---|---|
| Bachelor’s + |
36 Months (Which is in total 3 years) |
| Less than Bachelor’s |
60 Months (Which is in total 5 years) |
What does it mean that the experience needs to be within 8 years? It means that if we apply in April 2023 the experience needs to be within April 2015 and April 2023, however, it does not have to be consecutive 36 or 60 months.
How to Apply for the PMP exam:
First you need to apply for eligibility at www.pmi.org which is free and the response in within 5 working days of receiving the online application.
The response can be one of the following: Accepted, Rejected or Need Audit.
In case that your application randomly selected for Audit, you will need to submit supporting documents to the data in your eligibility application.
In case of accepted, you will have one year to take the exam.
To take the exam, you will need to schedule it online through www.pmi.org, You may take it online proctored from home as most of the people do, or by selecting a test room from those who are listed by PMI through the examination management company.
Exam Information
Type of Questions
The PMP Exam questions are multiple choice, drag and drop, … etc. Around one half of the questions targets process based project management while the other half targets Agile project management methodologies.
The difficult type of questions is that which is based on scenario analysis and best judgment determination.
Number of Questions
The PMP Exam is 180 questions, to be completed in 230 minutes which is 4 hours minus 10 minutes.
There are two 10 minutes breaks one after completion of 60 questions and the other after completion of 120 question.
The break times are not calculated as part of the 230 minutes.
The result is obtained directly, and it is a success or fail result not a percentage or grade.
PMP Exam Passing Score
The passing score of the exam is unknown, however people consider 62% would be the minimum, based on the last time when the exam success score was defined before more than 10 years, however it is a good practice that one gets 80% and above on the practice tests before taking the real exam.
How many times can one take the Exam?
Within the one-year eligibility period, the exam can be taken 3 times. The fees of the second and third attempts are usually discounted for PMI Members.
PMP Exam Fees
The PMP exam cost is US$405 for PMI members, or US$555 for nonmembers. I recommend my students to be members first, which costs US$139, so that they enjoy the membership benefits which includes downloading all PMI digital books including PMBOK 6th Ed, PMBOK 7th Ed and Agile for free, as well as repeating the exam if needed with significantly discounted fees. Membership is valid for one year.
The PMP certification is valid for 3 years and can be renewed by filling a PMI.org form showing that during these 3 years the certification holder had 60 PDUs (Professional Development Units) equivalent activities in project management like attending workshops, reading publications … etc. that you need to mention in your renewal application. The cost of renewing is US$60 for members, or US$150 for non-members, and the new PMP Certificate will be valid for another 3 years, and so forth.
How to Study for the PMP?
PMI describes the standard for project management in a book called PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge). The latest edition is 7.
In PMI.org website at This Link, we can see a pdf file showing the PMP Exam Contents (ECO description), on which all training material and exam preparation are based. The latest ECO was published in 2021, and it is the major reference on what will be in the Exam.
A second important link is the ( PMP Exam Reference List at pmi.org website ), it gives an answer on the most common question: which PMBOK to consider for the exam.
Here is an excerpt from that webpage on pmi.org:
“The exam is based on the PMP certification exam content outline (ECO), not the (PMBOK® Guide) or other reference books. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) - Seventh Edition will now be a reference to inform the development of the exam items. However, before any validated exam item is added to the exam, there is a very rigorous and thorough review and field test cycle.
This process takes multiple months.”
Most of PMP trainers including myself, recommend reading the following:
- The PMBOK 7th ed. as the latest edition.
- PMBOK 6th ed, as it is the latest in process-based project management. The Agile Practice Guide published by PMI.
- The Agile Practice Guide published by PMI.
- A brief reference or video lecture on Agile SCRUM project management.
- A book for PMP Exam Preparation for authors like Rita Mulcahy or Andy Crow which you may buy at www.amazon.com , making sure you select the latest editions.
About the PMBOK 7th Ed
The latest edition of PMI PMBOK is the seventh edition. It is available in several languages and can be downloaded free from PMI.org website if you gain PMI membership.
The main things described in PMBOK 7th edition is a set of 12 project management principles and 8 performance domains where these principles can be applied, and how to tailor this standard for your own
application field. It is around 200 pages book.
Principles
The 12 principles described in PMBOK 7th edition are:
- Be a diligent, respectful, and caring steward.
- Create a collaborative project team environment.
- Effectively engage with stakeholders.
- Focus on value.
- Recognize, evaluate, and respond to system interactions.
- Demonstrate leadership behaviors.
- Tailor based on context.
- Build quality into processes and deliverables.
- Navigate complexity.
- Optimize risk responses.
- Embrace adaptability and resiliency.
- Enable change to achieve the envisioned future state.
Performance Domains
The 8 performance domains on which the 12 principles are
applied are also described in PMBOK 7th edition and are:
- Stakeholders
- Team
- Development Approach and Life Cycle
- Planning
- Project Work
- Delivery
- Measurement
- Uncertainty
PMBOK 6th Ed,
The PMBOK 6th edition is more process based than PMBOK 7. It shows you the how to of project management, and this is why we think it is still needed for the PMP exam preparation, taking in consideration that PMBOK 7 was not meant to cancel PMBOK 6.
However, PMI newly published a guide which can be ordered and studied instead of PMBOK 6th edition to cover the process-based topics for the exam. It is called “Process Groups: A Practice Guide” and its link at amazon is: Process Groups: A Practical Guide.
PMBOK 6th edition is around 580 pages, and it describes 5 process groups in which any project may be performed and 10 Knowledge Areas (or experiences) which can be applied through these 5 process groups.
The PMBOK 6th Ed 5 Process Groups Are:
- Initiation
- Planning
- Executing
- Monitoring and Controlling
- Closing
The PMBOK 6th Ed 10 Knowledge Areas Are:
- Integration Management
- Scope Management
- Schedule Management
- Cost Management
- Quality Management
- Communication Management
- Resources Management
- Risk Management
- Procurement Management
- Stakeholder Management
PMBOK 6 Process Charts
49 Project Management Processes are distributed in these Process Groups and Knowledge areas to show in which process group and which knowledge area is a specific process applied.
And obviously this is demonstrated in a Process Chart which is as follows:
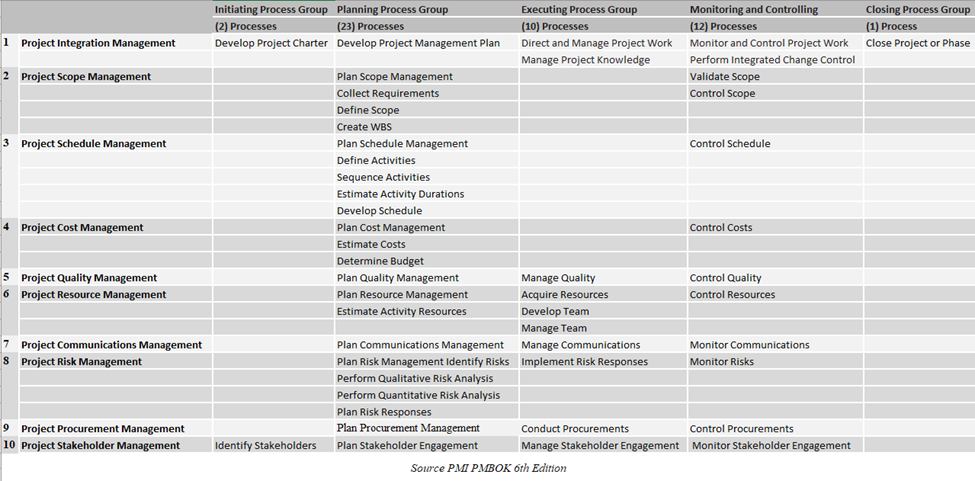
The Agile Practice Guide
The agile practice guide from PMI, describes agile project management concepts and techniques, it is the base for an Agile Exam from PMI called PMI Agile Certified Professional (PMI-ACP), however, it is important that you read it and understand it for the PMP exam as around half of the PMP exam question are Agile based.
Agile Manifesto
A group of 17 experts met in 2001 to exchange experiences on rapid project management and came up with the Agile Manifesto which mainly
defines 4 values and 12 principles on.
The 4 values are:
| Individuals and interactions | Over | processes and tools |
| Working software | Over |
comprehensive documentation |
| Customer collaboration | Over | contract negotiation |
| Responding to change | Over | following a plan |
The 12 Agile Principles are:
- Our highest priority is to satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software.
- Welcome changing requirements, even late in development. Agile processes harness change for the customer’s competitive advantage.
- Deliver working software frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference to the shorter timescale.
- Businesspeople and developers must work together daily throughout the project.
- Build projects around motivated individuals. Give them the environment and support they need and trust them to get the job done.
- The most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team is face-to-face conversation.
- Working software is the primary measure of progress.
- Agile processes promote sustainable development. The sponsors, developers, and users should be able to maintain a constant pace indefinitely.
- Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design enhances agility.
- Simplicity – the art of maximizing the amount of work not done – is essential.
- The best architecture, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams.
- At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly.
Hope you find this brief introduction beneficial and encouraging you to start your PMP Exam Prep. journey. All the good luck.
PMP Trainer Riad Thalji

Delivers His Training to top Organizations in the Middle East and North Africa

